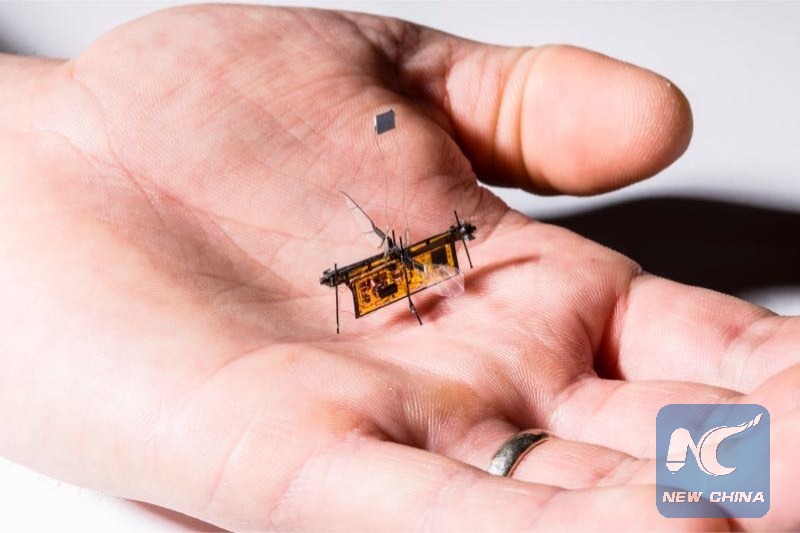

RoboFly, the first wireless insect-sized flying robot, is slightly heavier than a toothpick. (Credit: Mark Stone/University of Washington)
WASHINGTON, May 15 (Xinhua) -- Engineers at the University of Washington developed a robotic insect slightly heavier than a toothpick and powered by a laser beam.
The robot called "RoboFly" with independent flaps used a tiny onboard circuit that converts the laser energy into enough electricity to operate its wings, according to a news release of the university on Tuesday.
"Before now, the concept of wireless insect-sized flying robots was science fiction. Would we ever be able to make them work without needing a wire?" said Sawyer Fuller, an assistant professor with the university's Department of Mechanical Engineering. "Our new wireless RoboFly shows they're much closer to real life."
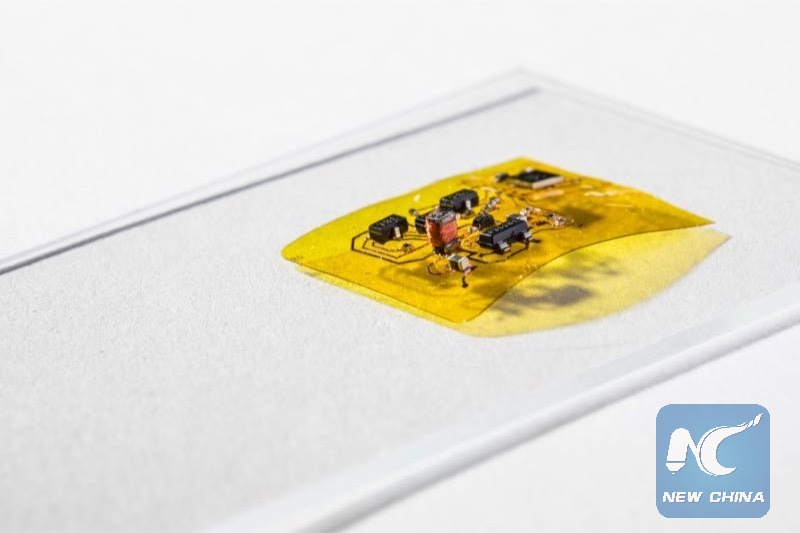
To make RoboFly wireless, the engineers designed a flexible circuit (yellow) with a boost converter (copper coil and black boxes at left) that boosts the seven volts coming from the photovoltaic cell into the 240 volts needed for flight. This circuit also has a microcontroller brain (black square box in the top right) that lets RoboFly control its wings. (Credit: Mark Stone/University of Washington)
The engineers said the engineering challenge was the flapping since wing flapping was a power-hungry process, and both the power source and the controller that directs the wings were too big and bulky to ride aboard a tiny robot.
So Fuller's previous robotic insect model had a leash, receiving power and control through wires from the ground.
Now, Fuller's team used a narrow invisible laser beam to power their robot. They pointed the laser beam at a photovoltaic cell, which is attached above RoboFly and converts the laser light into electricity.
However, the laser alone does not provide enough voltage to move the wings. So they designed a circuit that boosted the seven volts coming out of the photovoltaic cell up to the 240 volts needed for flight.
The controller sends voltage in waves to mimic the fluttering of a real insect's wings.
"It uses pulses to shape the wave," said Johannes James, a mechanical engineering doctoral student in the university.
"To make the wings flap forward swiftly, it sends a series of pulses in rapid succession and then slows the pulsing down as you get near the top of the wave. And then it does this in reverse to make the wings flap smoothly in the other direction," said James.
Also, the engineers added a micro-controller to the circuit to control over its wings.
"The micro-controller acts like a real fly's brain telling wing muscles when to fire," said Vikram Iyer, a doctoral student in the university' s Department of Electrical Engineering. "On RoboFly, it tells the wings things like 'flap hard now' or 'don't flap.'"
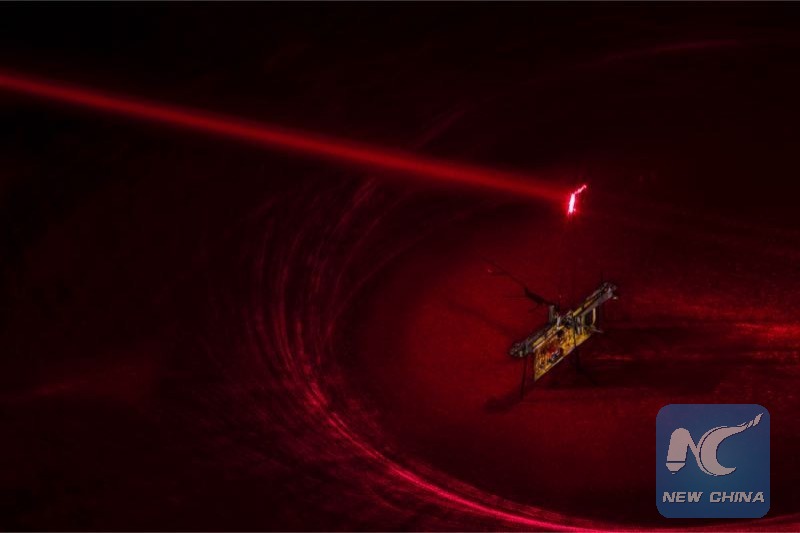

To power RoboFly the engineers pointed an invisible laser beam (shown here in red laser) at a photovoltaic cell, which is attached above the robot and converts the laser light into electricity. (Credit: Mark Stone/University of Washington)
For now, RoboFly can only take off and land. Once its photovoltaic cell is out of the direct line of sight of the laser, the robot runs out of power and lands.
But the team hoped to soon be able to steer the laser so that RoboFly could hover and fly around.
Future versions could use tiny batteries or harvest energy from radio frequency signals, according to engineers.
"I'd really like to make one that finds methane leaks," Fuller said. "If these robots can make it easy to find leaks, they will be much more likely to be patched up, which will reduce greenhouse emissions."
The team will present its findings on May 23 at the International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Brisbane, Australia.

